PID控制器
Published:
A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuously modulated control. A PID controller continuously calculates an error value as the difference between a desired setpoint (SP) and a measured process variable (PV) and applies a correction based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms (denoted P, I, and D respectively), hence the name.
mathematical form
The overall control function: $U(t)=k_{p}e(t)+k_{i}\int_{0}^{t}e(\tau)d\tau+k_{d}\frac{de(t)}{dt}$
举例调节水温:
通过误差e来调节输入u 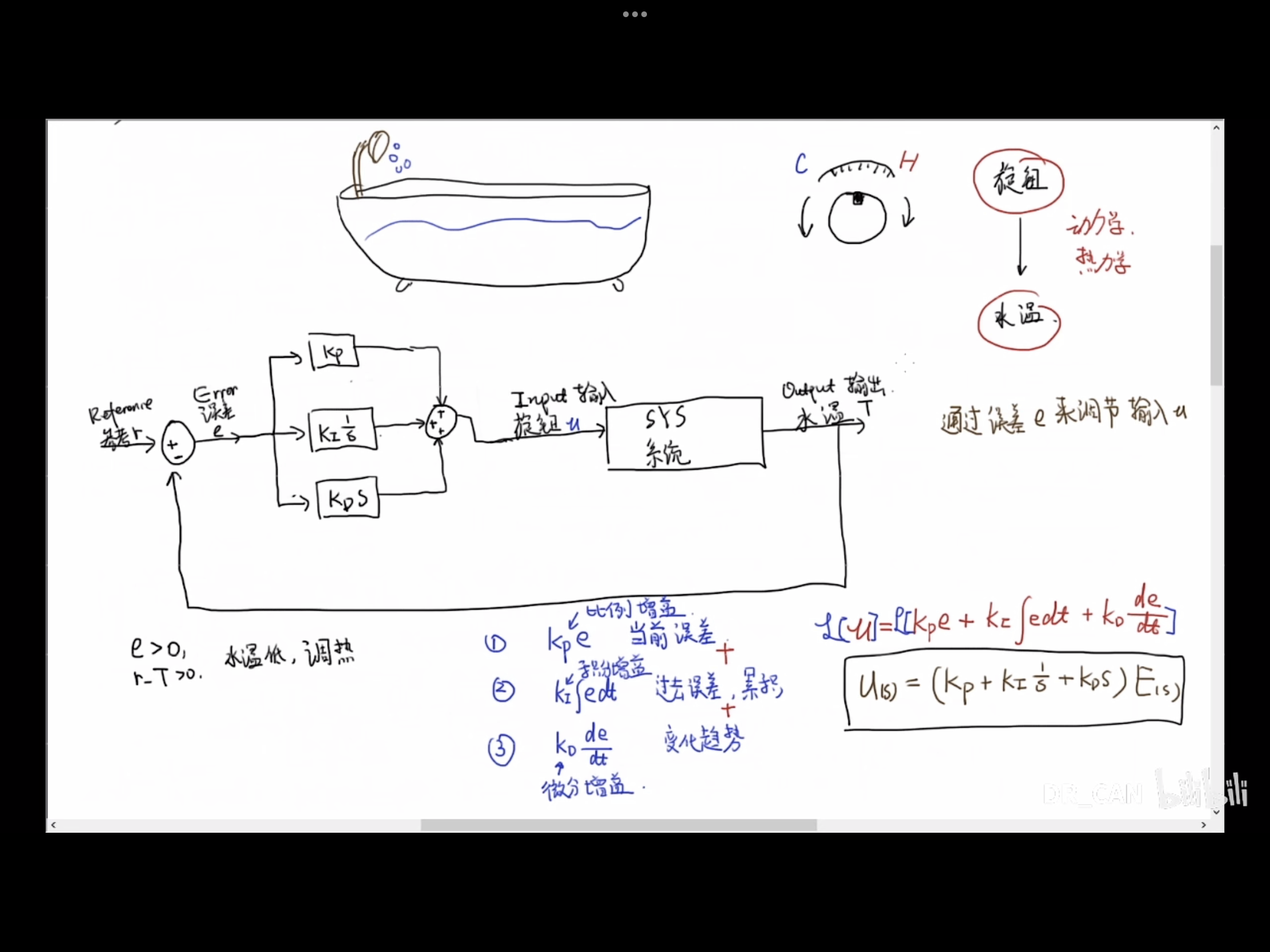 PD控制:提高稳定性,改善瞬态响应
PD控制:提高稳定性,改善瞬态响应
PI控制:改善稳态误差
PD控制与PI控制组成了PID控制
例题1
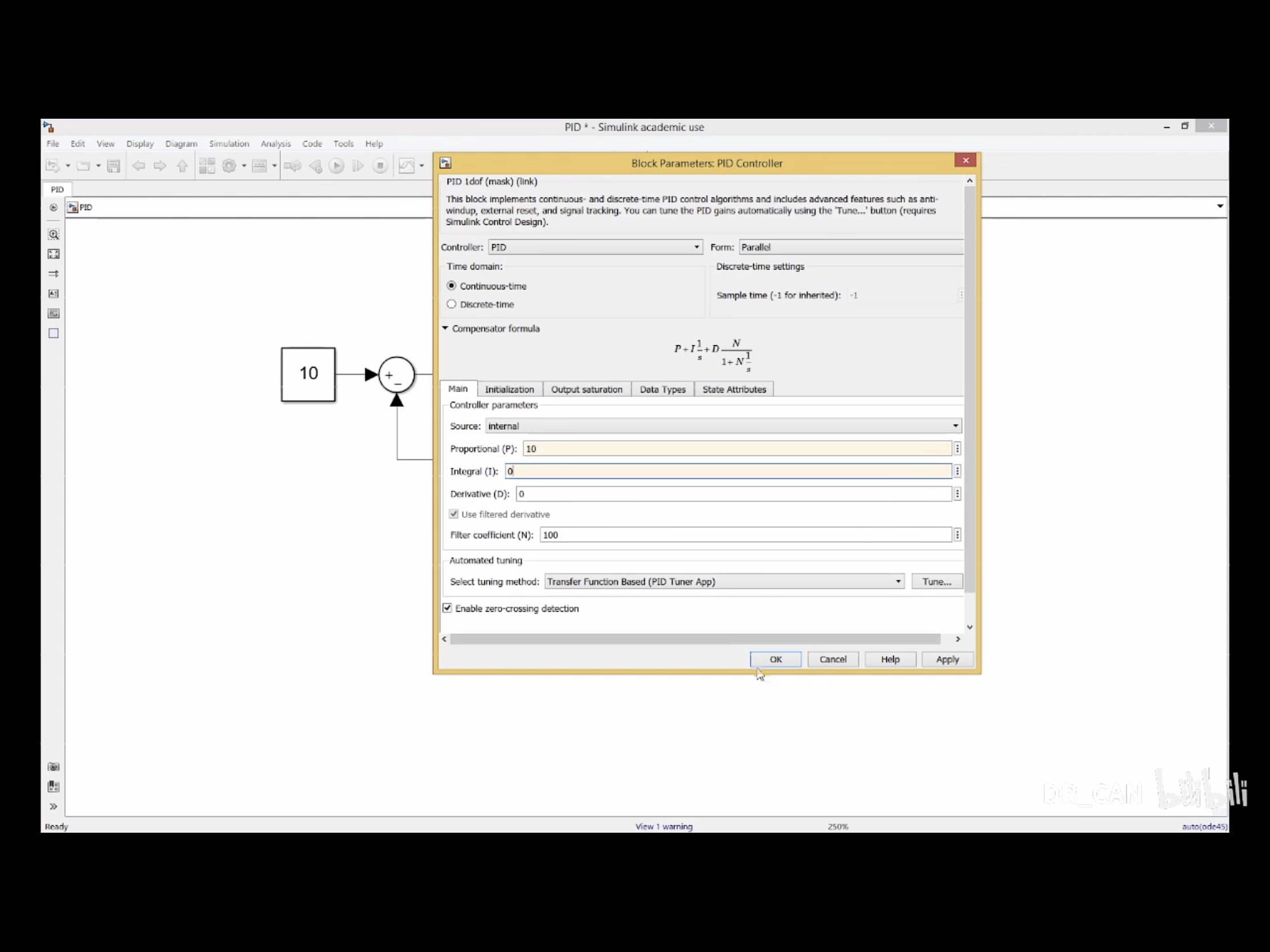
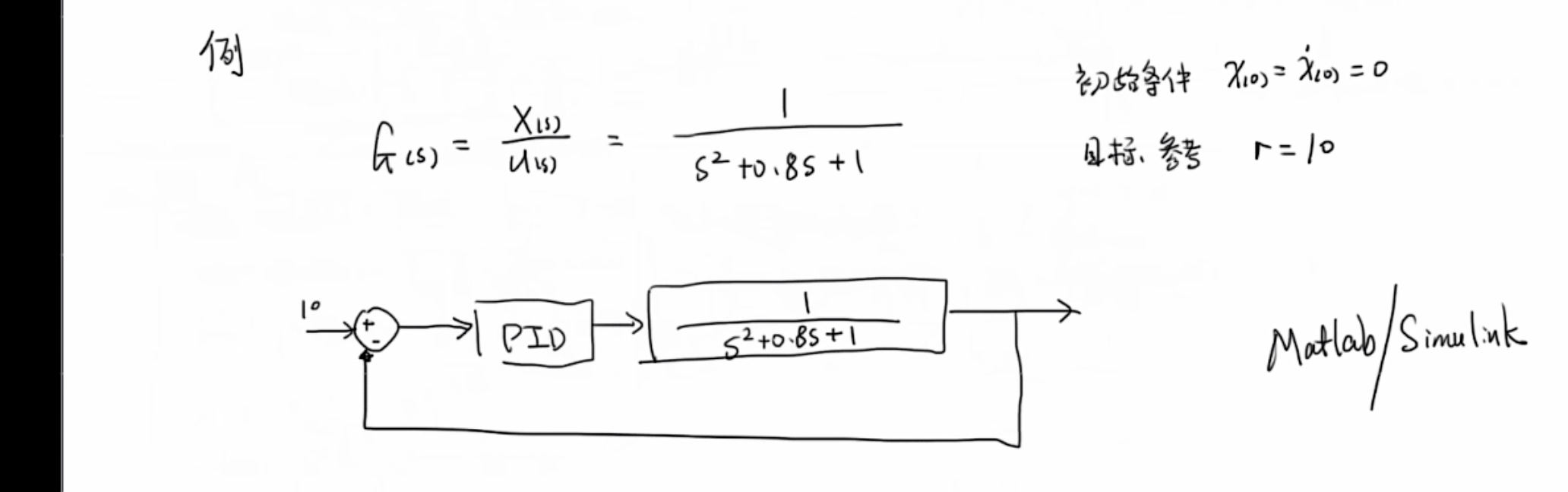 纯比例控制
纯比例控制
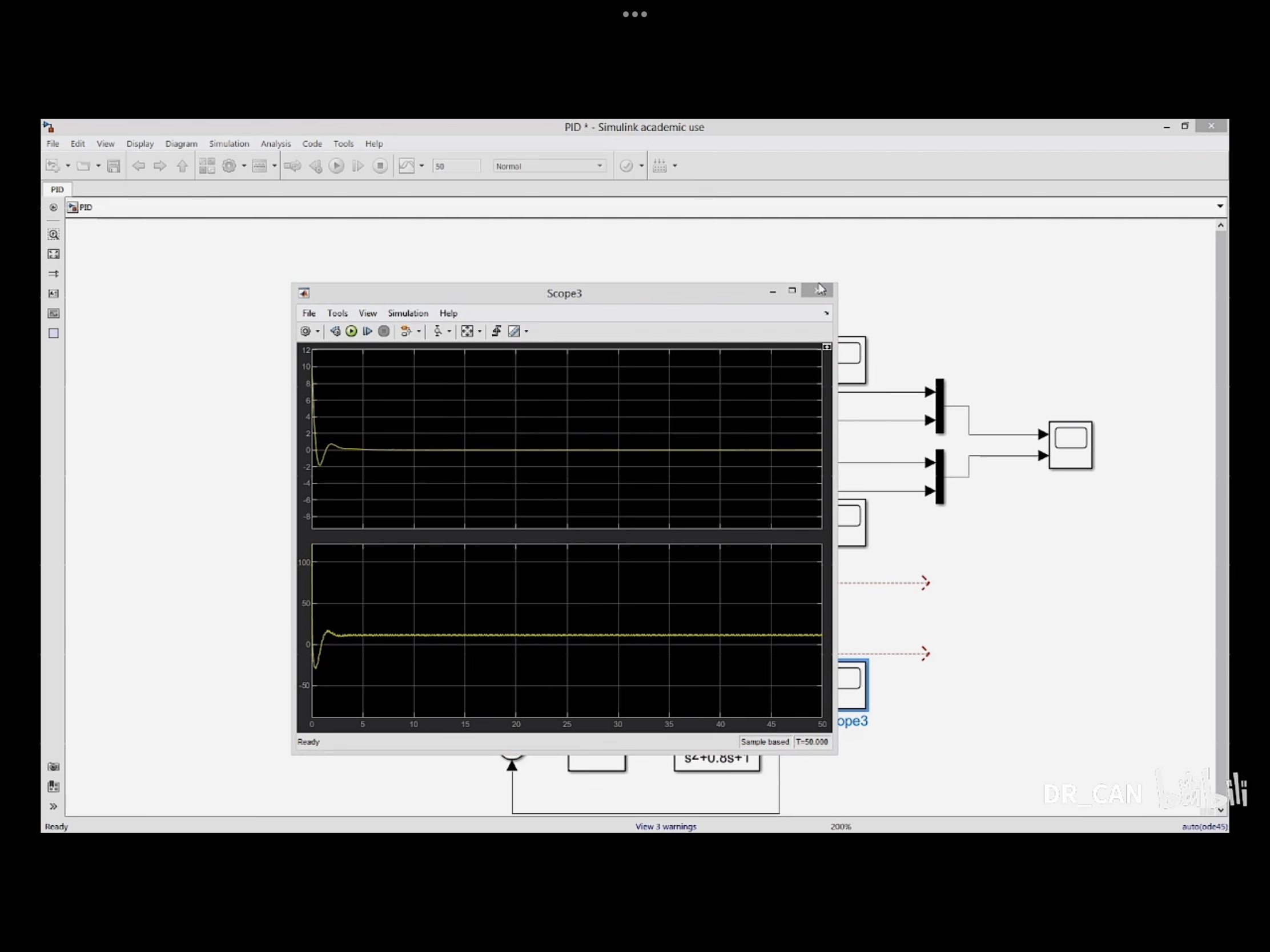
 结果
结果
无法完全消除稳态误差,误差大约在1左右
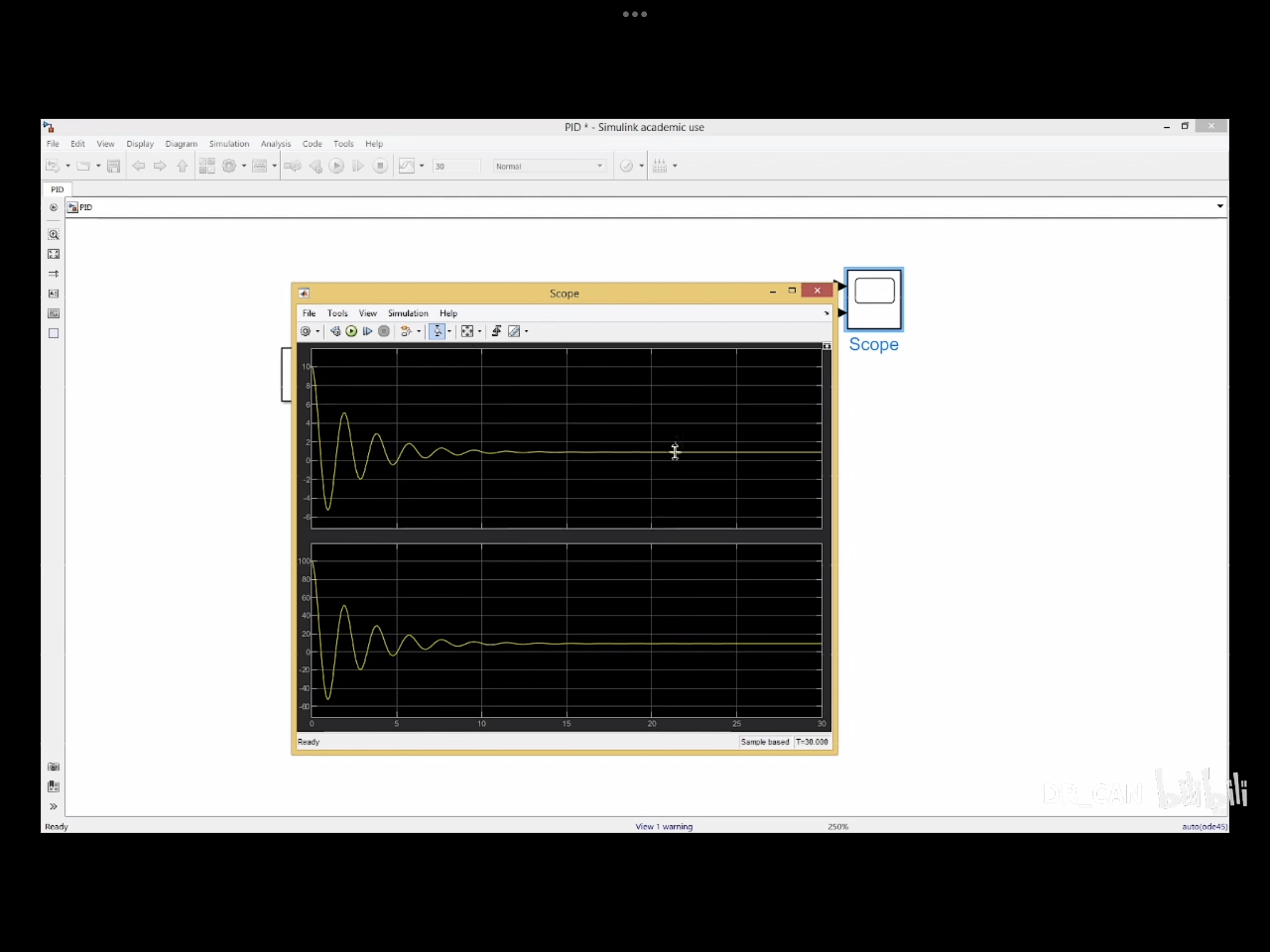 加上积分项
加上积分项
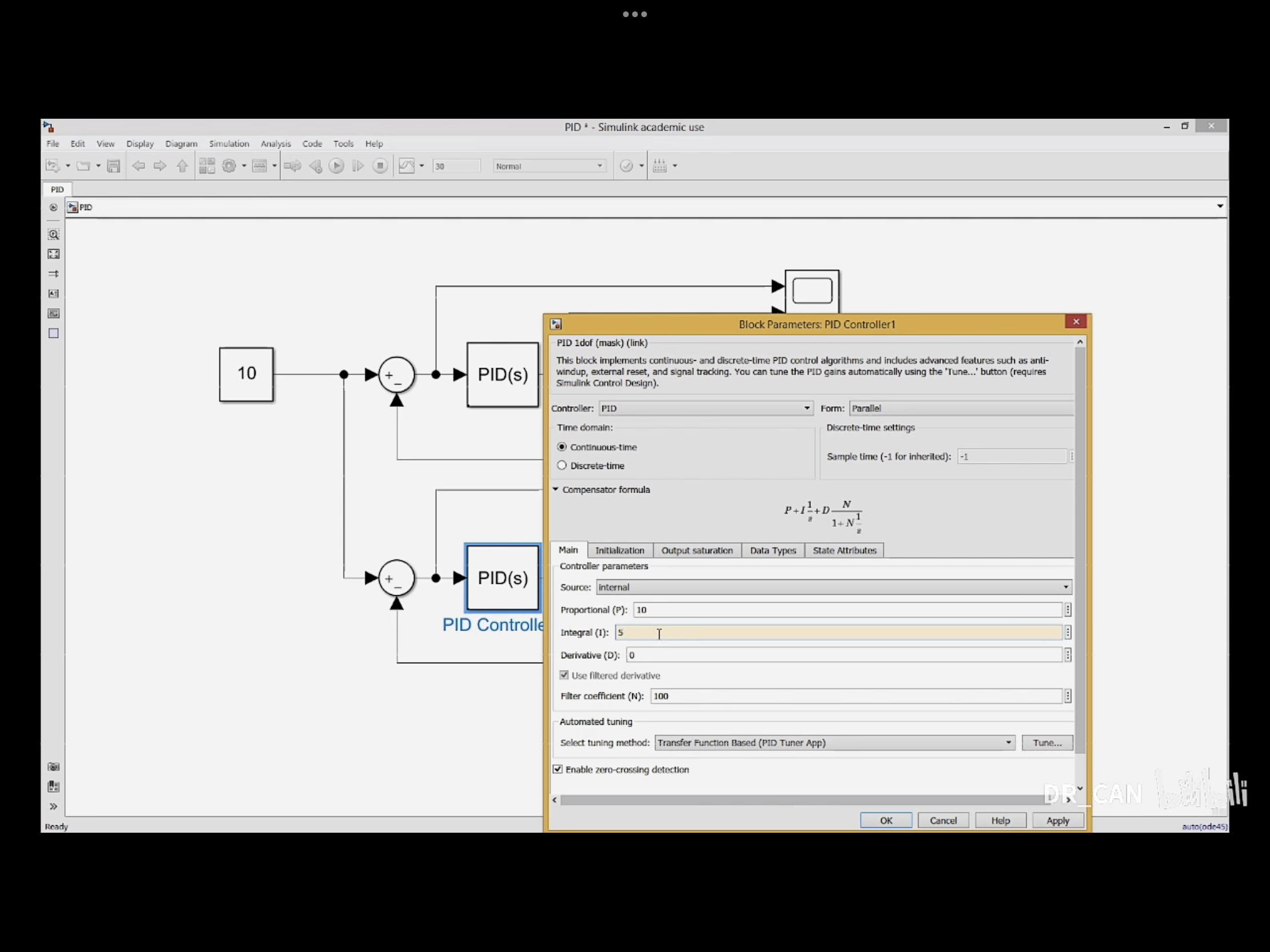 纯比例控制和比例积分控制在误差e和输入u的区别
纯比例控制和比例积分控制在误差e和输入u的区别
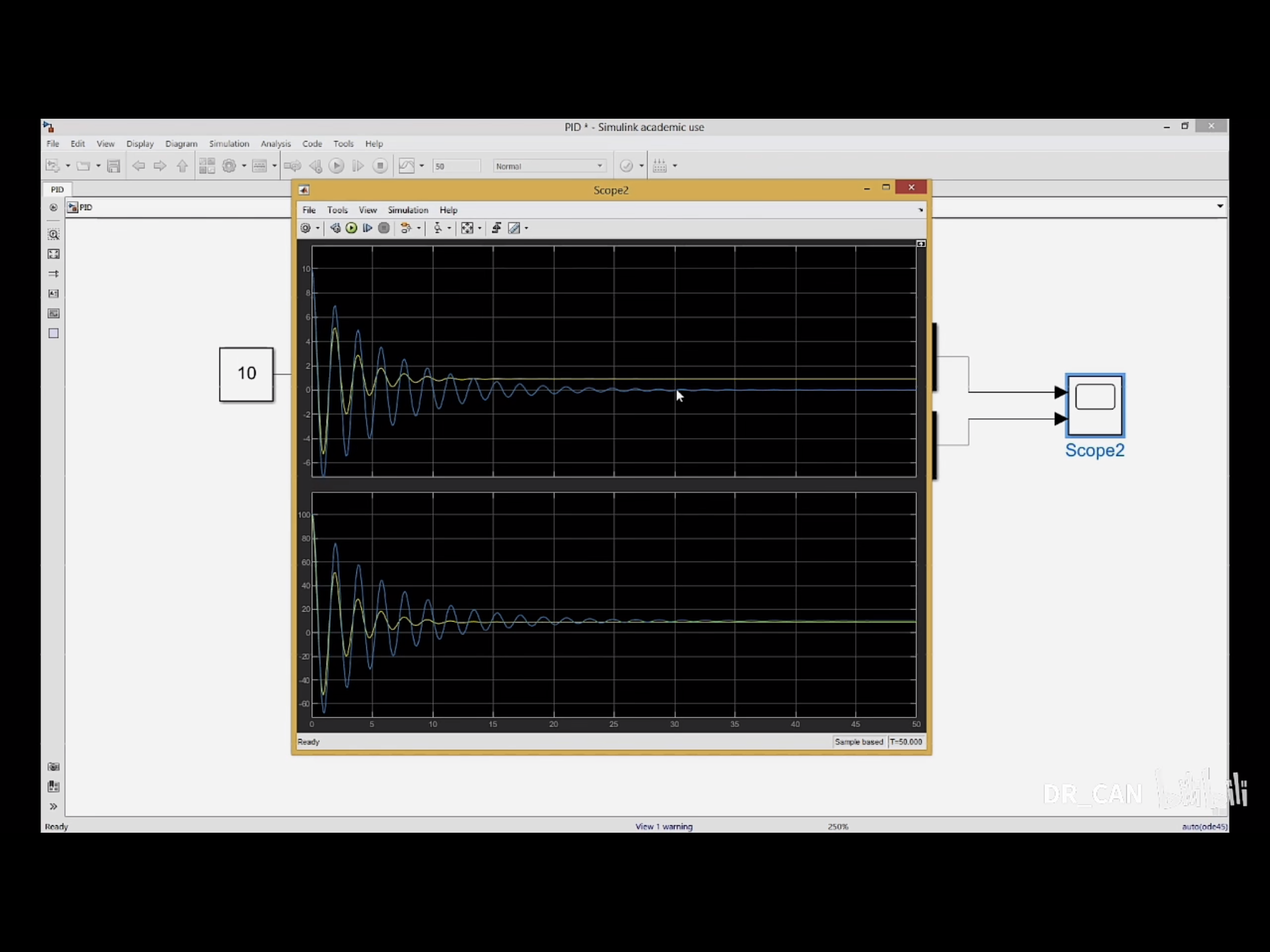 再加上微分项
再加上微分项
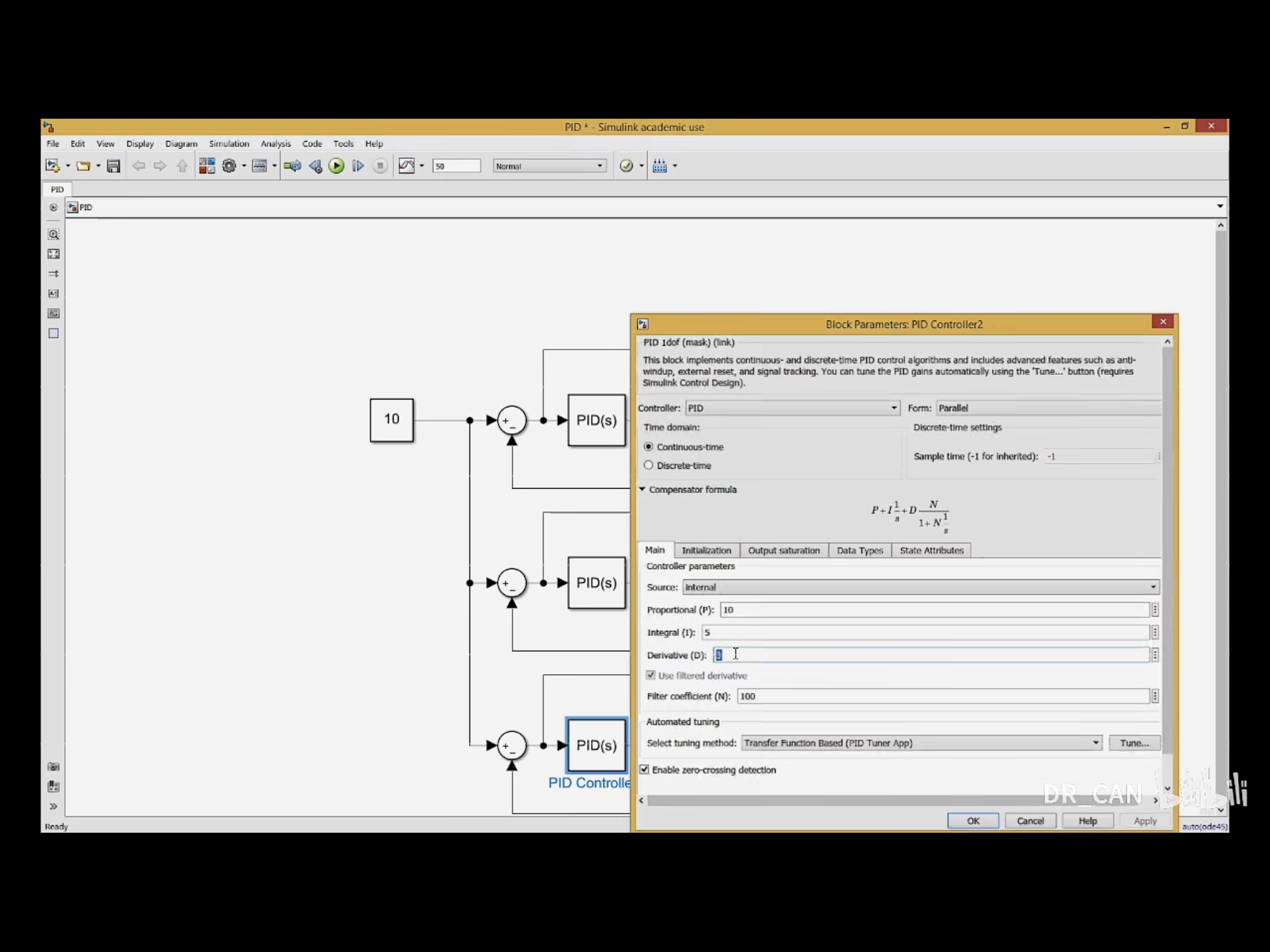 PID控制结果
PID控制结果